A lumbar strain is one of the most common reasons people experience lower back pain. If you’ve ever felt a sudden pull or tightness in your lower back after lifting something, twisting, or even just waking up the wrong way—you might be dealing with a lumbar strain.
In this 2025 guide, we’ll break down what a lumbar strain really is, what causes it, and how to spot the symptoms early. We’ll also share fast, effective ways to heal at home—plus tips to avoid future injuries. Whether your pain just started or has been hanging around for days, you’ll find clear answers and simple steps to start feeling better today.
Table of Contents
🚨 Looking for more information about Lower Back Pain? Check out our Top 7 Rehab Tools for Lower Back Pain Relief or other related posts throughout this site.
🏁 What Is a Lumbar Strain?
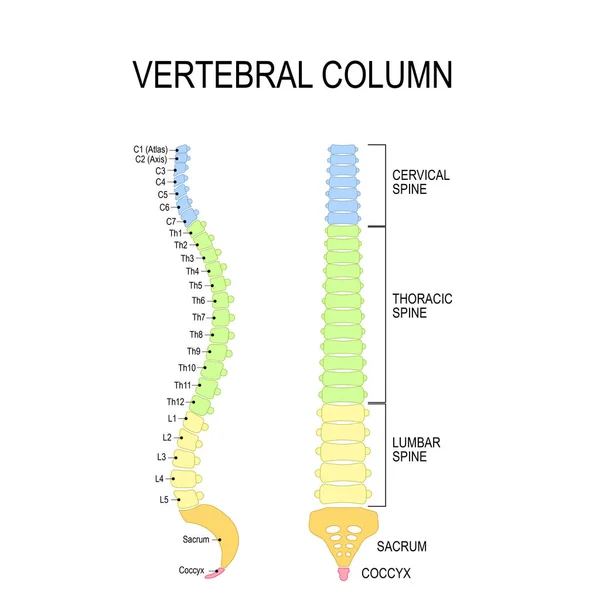
A lumbar strain is a stretched or torn muscle in the lower back. It happens when the muscles or tendons in your lumbar spine (lower back) are pushed beyond their limits. This can lead to pain, stiffness, swelling, or trouble moving.
It’s one of the most common back injuries and can affect anyone—from athletes and workers to people who simply bent the wrong way.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Your lumbar spine includes five vertebrae in your lower back, supported by muscles and soft tissues.
- A strain is different from a sprain. Strains affect muscles or tendons; sprains affect ligaments.
- Lumbar strains usually heal without surgery but can cause sharp pain or discomfort that lasts days or weeks.
Common signs you may have a lumbar strain:
- Trouble standing up straight or walking
- Sudden pain after lifting, twisting, or bending
- Muscle tightness or spasms
- Pain that worsens with movement but gets better with rest
⚖️ Common Causes of Lumbar Strain
A lumbar strain can happen suddenly or develop over time. It’s often caused by movements that place too much stress on the lower back muscles. Even simple daily activities—when done with poor posture or body mechanics—can lead to injury.
Here are the most common causes of lumbar strain:
- Sudden Increases in Activity
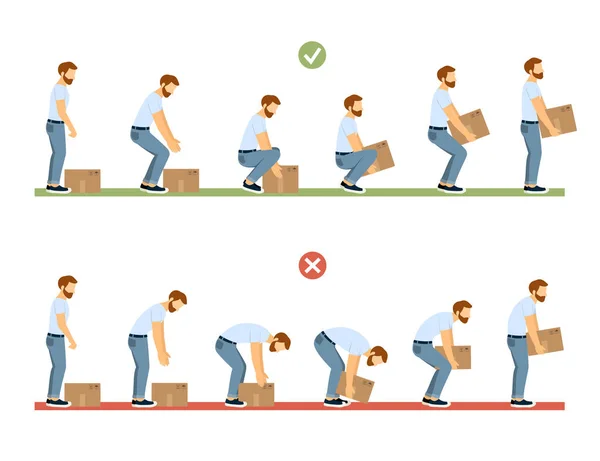
Jumping into intense workouts or yard work after being inactive can shock your lower back muscles. - Lifting Heavy Objects Incorrectly
Using your back instead of your legs when lifting puts major strain on the lumbar muscles. - Sudden Twisting or Bending Movements
Quick or awkward movements, especially while turning or reaching, can stretch muscles beyond their limits. - Overuse or Repetitive Motions
Jobs or activities that involve frequent bending, lifting, or twisting (like warehouse work or sports) can cause strain over time. - Poor Posture
Slouching while sitting or standing adds extra stress to the lower back, especially if done for hours at a time. - Weak Core Muscles
Your core supports your spine. Weak abdominal or back muscles increase the risk of strain.
🟡 Symptoms of a Pulled Lower Back Muscle
Recognizing the signs of a lumbar strain early can help you avoid making the injury worse. While some people feel sharp pain right away, others may notice tightness or discomfort that builds over time.
Here are the most common symptoms of a pulled lower back muscle:
- Sharp or Aching Pain in the Lower Back
This pain is usually felt on one side of the lower back and may come on suddenly after activity. - Stiffness and Limited Movement
You may have trouble bending, twisting, or standing up straight without pain. - Muscle Spasms
The muscles in your lower back may feel like they’re tightening or cramping on their own. - Pain That Gets Worse with Movement
Walking, lifting, or even standing for long periods can increase the pain. Lying down often brings relief. - Swelling or Tenderness
The injured area may feel sore to the touch and could appear slightly swollen or warm.
🔍 When to See a Doctor or Physical Therapist
Most lumbar strains improve with rest, light movement, and at-home care. However, if you experience any of the following, it’s time to see a healthcare provider:
- Difficulty controlling your bladder or bowels
- Pain that lasts more than 2 weeks
- Numbness or tingling in the legs
- Pain after a fall or accident
🩹 How to Heal a Lumbar Strain Fast
Most lumbar strains heal within a few days to a few weeks—especially with the right care. The key is knowing what to do (and what to avoid) in the first 48 hours and beyond.
Here are the best ways to recover quickly from a lumbar strain:
1. Rest (But Don’t Stay in Bed Too Long)
Take it easy for the first 1–2 days, especially if movement increases your pain. But avoid long periods of bed rest—gentle movement helps reduce stiffness and speeds up healing.
2. Apply Ice and Heat
- First 48 hours: Use ice packs (15–20 minutes at a time) to reduce swelling and numb pain.
- After 2 days: Switch to heat packs or warm baths to relax muscles and improve blood flow.
3. Try Over-the-Counter Pain Relief
Anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Aleve) can reduce pain and swelling.
4. Gentle Stretching and Movement
After the initial pain subsides, try light stretches or short walks to keep your muscles flexible. Avoid anything that causes sharp pain.
5. Use Supportive Tools
A lumbar support brace or cushion can help relieve pressure while sitting or standing. These tools should be used short-term and alongside movement, not as a permanent fix.
⚠️ What to Avoid:
- Jumping back into workouts too soon
- Heavy lifting or twisting motions
- Prolonged sitting or standing without breaks
✅ Do’s and ❌ Don’ts for Healing Lumbar Strain
| ✅ Do’s | ❌ Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Rest for the first 1–2 days | Stay in bed for too long |
| Apply ice (15–20 min) during first 48 hours | Use heat too early (can increase swelling) |
| Switch to heat after 2 days | Ignore sharp or worsening pain |
| Take OTC pain meds (as directed) | Overuse painkillers or rely on them alone |
| Do light stretching and walking | Resume workouts or lifting too soon |
| Use lumbar support for short-term relief | Wear a back brace all day, every day |
| Practice good posture while sitting/standing | Slouch at your desk or couch |
| Listen to your body and move gently | Push through pain during recovery |
🏋️ Best At-Home Exercises for Lumbar Strain Recovery
Once the initial pain from a lumbar strain starts to fade (usually after a few days), gentle exercises can help speed up recovery. These movements improve flexibility, reduce stiffness, and strengthen the muscles that support your lower back.
⚠️Important: If any of these exercises cause sharp pain, stop right away and consult a healthcare provider.
1. Pelvic Tilts
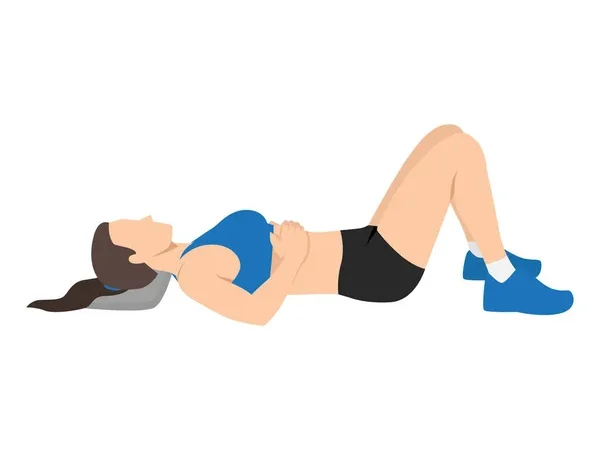
How to do it:
Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Gently tighten your stomach muscles and flatten your lower back against the floor. Hold for 5 seconds, then relax.
Reps: 10–15 reps, 2 sets
✅Benefit: Improves core stability and relieves back tension
2. Knee-to-Chest Stretch
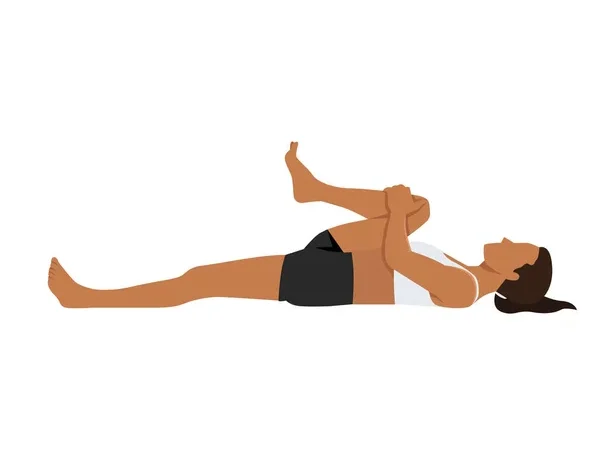
How to do it:
Lie on your back. Bring one knee up toward your chest, holding your leg with both hands. Hold for 20–30 seconds, then switch legs.
Reps: 2–3 times per leg
✅Benefit: Stretches the lower back and relieves tightness
3. Cat-Cow Stretch
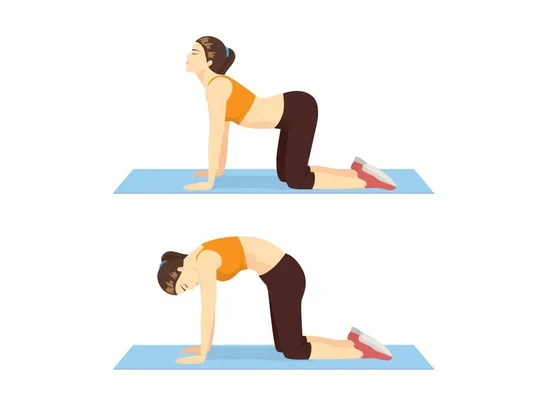
How to do it:
Get on your hands and knees. Arch your back up (like a cat) and then slowly dip it down while lifting your head and tailbone (like a cow).
Reps: 10–15 reps
✅Benefit: Gently mobilizes the spine and reduces stiffness
🛑 How to Prevent Future Lumbar Strains
Once you’ve recovered from a lumbar strain, the next step is keeping it from coming back. Many lower back injuries happen because of weak muscles, poor posture, or bad lifting habits. The good news? Small changes in your daily routine can make a big difference.
Here are 7 simple ways to prevent another lumbar strain:
1. Strengthen Your Core
A strong core supports your spine. Add exercises like planks, bird-dogs, and pelvic tilts to your weekly routine.
2. Stretch Regularly
Tight hamstrings, hips, or back muscles can pull on your spine. Gentle stretching a few times a week improves flexibility and lowers injury risk.
3. Use Proper Lifting Techniques
Always bend at the knees, not the waist. Keep heavy items close to your body and avoid twisting while lifting.
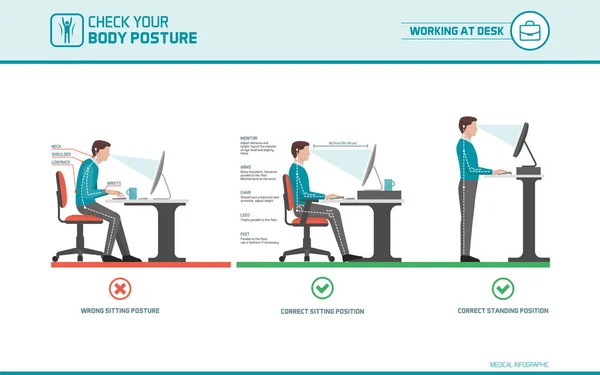
4. Watch Your Posture
Whether you’re sitting at a desk or standing in line, keep your back straight and shoulders relaxed. Consider a lumbar support cushion if you sit for long periods.
5. Take Movement Breaks
Sitting or standing too long in one position can strain your lower back. Take short breaks to stretch or walk every 30–60 minutes.
6. Warm Up Before Activity
Before lifting, exercising, or doing yard work, warm up your muscles with light movement or dynamic stretching.
7. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Extra weight adds pressure to your spine and increases the chance of back injuries. A balanced diet and regular movement help keep your back healthy.
✅ Conclusion: Take Care of Your Back, Starting Today
A lumbar strain can be painful—but with the right care, most people recover quickly and fully. Knowing what causes it, how to spot the symptoms, and what steps to take for healing puts you in control of your recovery.
Whether you’re dealing with lower back pain right now or want to prevent future injuries, remember: small, daily habits make a big impact. Strengthen your core, move with intention, and listen to your body.
If your pain doesn’t improve or gets worse, don’t wait—talk to a medical professional to rule out more serious issues.
✅ Your Next Steps:
- Bookmark this 2025 lumbar strain guide for quick reference
- Try the gentle exercises shared above
- Use our Do’s and Don’ts chart as a daily guide