When it comes to managing pain and promoting recovery, heat and cold therapy are two of the most commonly used methods. Whether you’re recovering from an injury, dealing with chronic pain, or just looking to relieve muscle tension, knowing when and how to use heat vs cold therapy can make a big difference in your healing process. In this blog post, we’ll explore the benefits, application methods, and safety precautions of both heat and cold therapy to help you decide which one is best for your needs.
Table of Contents
How Heat and Cold Therapy Work
Heat and cold therapy Are simple and effective ways to manage pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing. Each method works differently, and choosing the right one depends on the type of pain or injury you’re experiencing.
How Heat Therapy Works
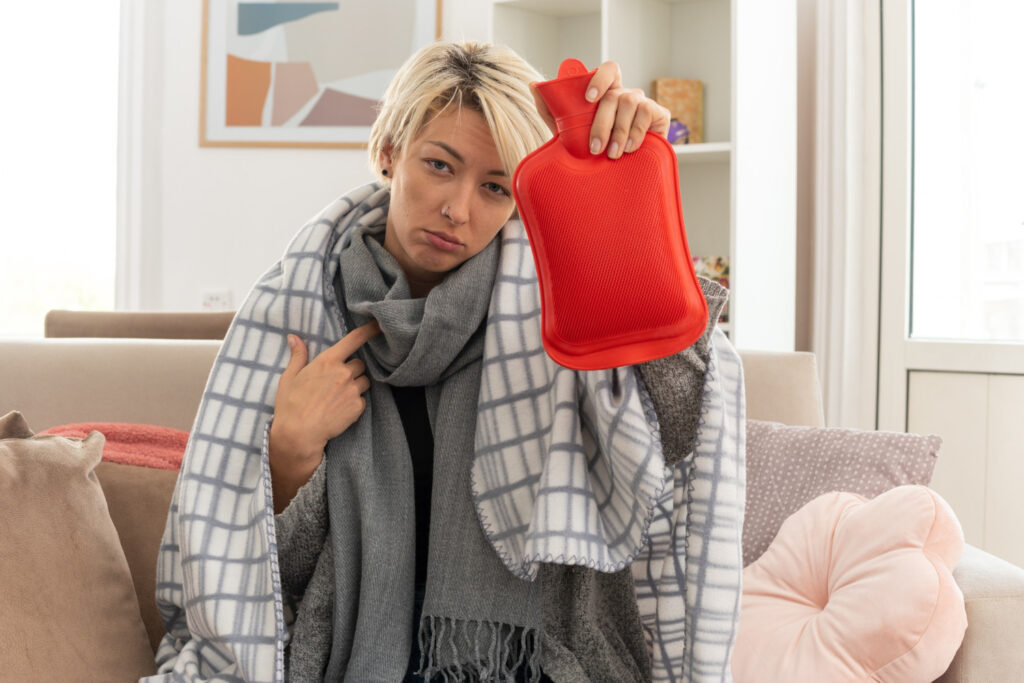

Heat therapy helps by increasing blood flow to the affected area. When heat is applied, blood vessels expand (vasodilation), allowing more oxygen and nutrients to reach muscles and joints. This helps:
- Relax tight muscles and reduce stiffness.
- Improve circulation, which promotes healing.
- Soothe chronic pain from conditions like arthritis and muscle tension.
Types of Heat Therapy:
- Dry heat – Heating pads, heat wraps, infrared lamps.
- Moist heat – Warm towels, hot baths, steam therapy.
💡 Best for: Chronic pain, muscle stiffness, joint pain, and relaxation before activity.
How Cold Therapy Works
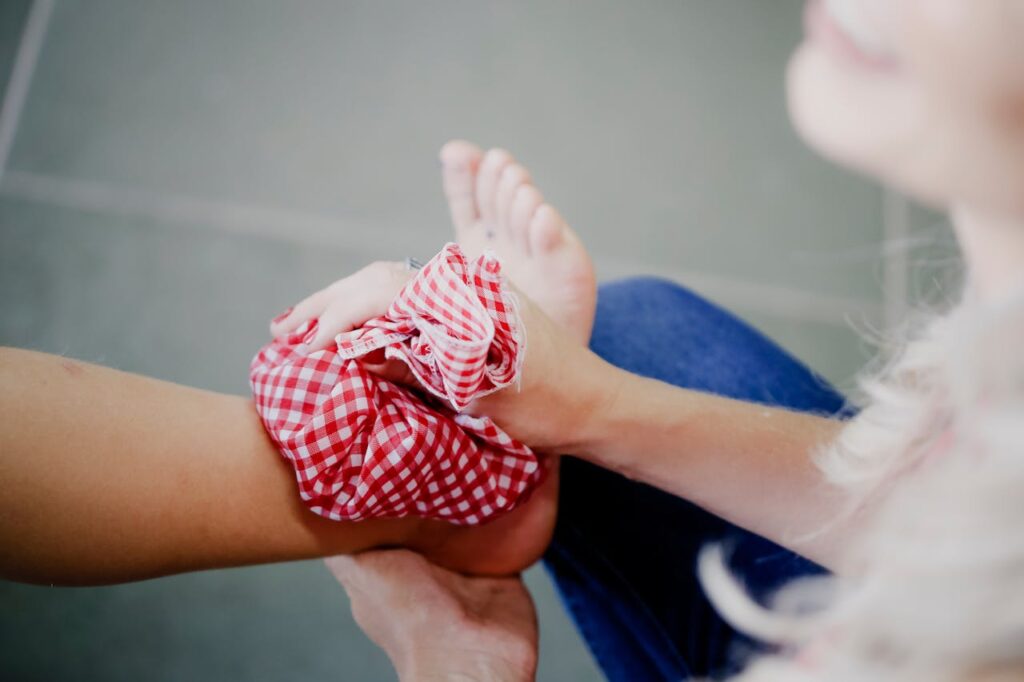

Cold therapy works by reducing blood flow to the affected area. When cold is applied, blood vessels constrict (vasoconstriction), which helps:
- Reduce swelling and inflammation after an injury.
- Numb pain by slowing nerve signals.
- Prevent further tissue damage in acute injuries.
Types of Cold Therapy:
- Ice packs – Reusable gel packs, frozen vegetables, or homemade ice packs.
- Cold compresses – Damp, cold towels or cooling gel wraps.
- Cryotherapy – Ice baths or whole-body cryotherapy sessions.
💡 Best for: Acute injuries, swelling, bruising, and post-workout soreness.
Key Differences Between Heat and Cold Therapy


- Heat therapy increases circulation and relaxes muscles, making it ideal for chronic pain.
- Cold therapy reduces inflammation and numbs pain, making it best for fresh injuries.
Choosing the right therapy depends on whether you need increased blood flow (heat) or reduced swelling (cold).
Best Uses for Heat Therapy
Heat and cold therapy can be effective ways to relieve pain, but heat therapy is particularly beneficial for certain conditions. By increasing blood flow and relaxing muscles, heat therapy helps with chronic pain, stiffness, and tension.
When to Use Heat Therapy

Heat therapy is most effective for chronic pain and muscle relaxation. It works best when the goal is to increase circulation and reduce stiffness rather than control swelling.
Common Uses for Heat Therapy:
- Chronic Pain Relief
- Ideal for arthritis, lower back pain, and joint stiffness.
- Helps loosen tight muscles and improve flexibility.
- Muscle Relaxation & Stiffness
- Useful for neck pain, shoulder tension, and muscle cramps.
- Increases blood flow, allowing muscles to relax.
- Pre-Exercise Warm-Up
- Applying heat before a workout helps prepare tight or sore muscles.
- Reduces the risk of strain or injury.
- Menstrual Cramp Relief
- Heat therapy can ease discomfort by relaxing uterine muscles.
- A heating pad or warm compress can provide quick relief.
- Stress-Related Pain & Tension Headaches
- Heat helps relieve tension in the shoulders, neck, and upper back.
- Warm compresses can also soothe sinus pressure.
Best Heat Therapy Methods



There are several ways to apply heat therapy, depending on the type of pain:
- Heating Pads & Electric Blankets – Great for targeted relief on the lower back, neck, or joints.
- Warm Baths & Hot Showers – Ideal for full-body relaxation and muscle pain.
- Heat Wraps & Gel Packs – Convenient for on-the-go relief.
- Warm Towels & Compresses – Effective for localized pain and headaches.
💡 Pro Tip: Avoid using heat therapy on recent injuries or inflamed areas, as it can worsen swelling.
Final Thoughts
Heat therapy is a great option for chronic pain, muscle stiffness, and stress relief. It works best when applied for 15–20 minutes at a time. If you’re unsure whether to use heat or cold therapy, remember: Use heat for stiffness and tension, and cold for swelling and acute injuries.
Best Uses for Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy are proven methods for pain relief, but cold therapy is particularly effective for reducing inflammation, numbing pain, and preventing further injury. Whether you’re dealing with a fresh injury, post-exercise soreness, or chronic inflammation, using cold therapy correctly can speed up recovery and minimize discomfort.
1. Treating Acute Injuries
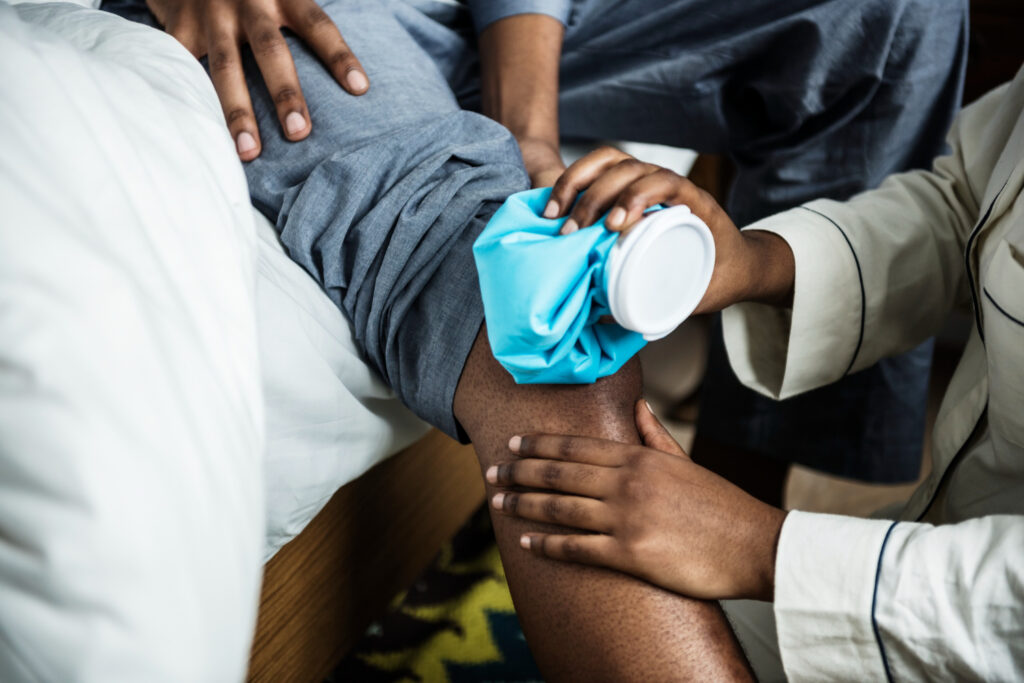

Cold therapy is most effective for acute injuries, such as:
- Sprains and strains (ankle sprains, wrist injuries, muscle pulls).
- Bruises and contusions from impact injuries.
- Post-surgical swelling (with doctor approval).
Applying ice immediately after an injury reduces swelling, bruising, and pain by restricting blood flow to the affected area.
💡 How to Use It: Apply an ice pack for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours during the first 48 hours after an injury. Always wrap ice in a towel to prevent skin damage.
2. Reducing Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling is the body’s natural response to injury, but excessive inflammation can delay healing. Cold therapy minimizes swelling by constricting blood vessels and slowing cellular activity.
💡 Best for:
- Tendonitis (e.g., tennis elbow, Achilles tendonitis).
- Bursitis (joint inflammation in the shoulder, hip, or knee).
- Arthritis flare-ups that cause swelling.
3. Numbing Pain and Soreness
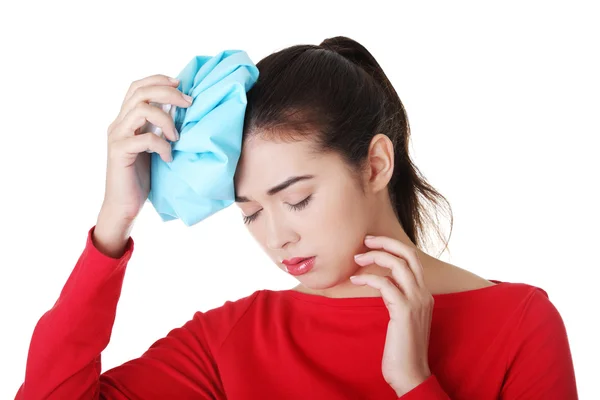

Cold therapy helps numb pain by slowing nerve signals, making it useful for:
- Headaches and migraines (apply a cold pack to the back of the neck).
- Muscle soreness after workouts (reduces delayed onset muscle soreness, or DOMS).
- Joint pain relief for chronic conditions like osteoarthritis.
💡 How to Use It: Apply an ice pack or cooling gel for 10-15 minutes to the painful area.
4. Post-Workout Recovery

Athletes and fitness enthusiasts often use cold therapy for muscle recovery after intense workouts. Ice baths or cryotherapy sessions help:
- Reduce muscle inflammation and speed up recovery.
- Prevent excessive soreness after heavy training.
- Refresh and rejuvenate tired muscles.
💡 How to Use It: Try 10-15 minutes in an ice bath after a tough workout or long run.
5. Managing Chronic Pain Conditions
Cold therapy isn’t just for sudden injuries—it can also provide relief for chronic pain conditions, including:
- Lower back pain (especially if inflammation is present).
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (numbs pain from repetitive strain injuries).
- Sciatica (helps with nerve pain flare-ups).
💡 How to Use It: Apply cold therapy to the affected area when inflammation or pain flares up for quick relief.
Final Thoughts
Cold therapy is best for acute injuries, swelling, muscle soreness, and pain relief. It works by reducing blood flow, numbing pain, and preventing excessive inflammation.
✅ Use cold therapy for: fresh injuries, post-workout recovery, and swelling reduction.
❌ Avoid cold therapy if: you have circulation issues, nerve damage, or extreme sensitivity to cold.
For chronic pain relief, alternating heat and cold therapy (contrast therapy) may be the best approach. Always consult a healthcare professional if you’re unsure which treatment to use.
Effectiveness for Pain Relief
Choosing heat vs cold therapy depends on the type of pain and its cause.
- Cold therapy is more effective for acute injuries, swelling, and nerve pain because it reduces inflammation and numbs pain.
- Heat therapy is more effective for chronic pain, muscle stiffness, and joint tightness by increasing blood flow and relaxing muscles.
- For post-exercise soreness, start with cold therapy immediately after the workout to reduce inflammation, then switch to heat therapy the next day to relax muscles.
- For joint pain, use cold therapy for inflammation (e.g., arthritis flare-ups) and heat therapy for stiffness (e.g., osteoarthritis).
Key takeaway: Use cold therapy for new injuries and swelling, and heat therapy for chronic pain and stiffness for the best relief.
Recovery and Healing Time
Using heat and cold therapy correctly can significantly impact how fast your body heals from injuries, soreness, and chronic pain conditions. While both therapies aid recovery, they work in different ways and should be applied at the right time for maximum effectiveness.
- Cold therapy speeds up recovery from acute injuries by reducing swelling but should not be overused.
- Heat therapy promotes long-term healing by increasing blood flow and relaxing muscles.
- For the fastest recovery, use cold therapy in the first 48 hours, then transition to heat therapy once inflammation decreases.
By using heat and cold therapy appropriately, you can optimize your body’s natural healing process and recover faster from injuries, soreness, and chronic pain.
Application Methods and Popular Products

For effective heat and cold therapy, choosing the right application method and product is key to maximizing pain relief and recovery:
- Cold Therapy:
- Use ice packs, gel packs, or cold wraps for acute injuries like sprains and strains.
- Ice baths or cryotherapy machines are ideal for muscle recovery after intense exercise.
- Best for reducing swelling and numbing pain in the first 48 hours after an injury.
- Heat Therapy:
- Use heating pads, hot water bottles, or heat wraps to relieve muscle stiffness and chronic pain.
- Warm baths and steam therapy are excellent for full-body relaxation.
- Best for increasing circulation and relaxing tense muscles.
Popular products include TheraPearl Ice Packs, PureRelief Heating Pads, and ThermaCare Heat Wraps, offering targeted relief for specific areas or full-body treatment.
Safety Risks and Precautions
Both heat and cold therapy are effective pain relief methods, but they must be used with caution to avoid risks:
- Cold therapy can cause frostbite, ice burn, or nerve damage if applied too long or directly to the skin. Always wrap ice and limit use to 15-20 minutes.
- Heat therapy can lead to burns, dehydration, or overheating if the heat source is too hot or used for too long. Always check the temperature and use for short periods.
- General precautions include avoiding heat or cold on open wounds, monitoring skin, and consulting with a healthcare provider if you have specific health conditions.
By following these guidelines, you can safely benefit from heat or cold therapy without the risk of harm.
Cost and Convenience
When comparing heat and cold therapy options:
- Cold therapy can be highly affordable, with ice packs and gel packs being inexpensive, while cold therapy machines are pricier but provide continuous and targeted treatment.
- Heat therapy has both low-cost options like hot water bottles and DIY heating pads, as well as more expensive products like electric heating pads and moist heat therapy options.
- In terms of convenience, both therapies offer easy-to-use solutions at home, but cold therapy machines and heating pads provide hands-free use and longer-lasting comfort.
Ultimately, the cost and convenience of each option depend on the level of investment and the type of pain relief you’re seeking.
Comparison of Cost and Convenience
| Product | Price Range | Convenience |
|---|---|---|
| Ice Packs/Gel Packs | $5 – $15 | Easy to use, portable, and low-maintenance. |
| Cold Therapy Machines | $100 – $300 | High-tech, hands-free, but bulky. |
| Hot Water Bottles | $5 – $15 | Portable but requires refilling. |
| Heating Pads | $20 – $80 | Convenient, portable, and adjustable. |
| Moist Heat Products | $30 – $100 | Deeper relief, but pricier. |
Conclusion
When it comes to heat and cold therapy, both methods have their own unique benefits, and the right choice largely depends on your specific pain relief needs. Cold therapy is ideal for reducing inflammation and treating acute injuries, while heat therapy works wonders for chronic pain and muscle relaxation.
By understanding the best uses, effectiveness, and application methods for both heat and cold therapy, you can make informed decisions that enhance your recovery process. Remember to always consider safety precautions to avoid any risks like burns or frostbite, and choose products that fit your budget and convenience preferences.
Whether you’re dealing with an injury, muscle soreness, or joint pain, incorporating heat or cold therapy into your treatment routine can offer significant relief. With the right approach, these therapies can be powerful tools in your recovery and pain management journey.
Recommended Products for Heat and Cold Therapy
Cold Therapy Products
- Braceability Cold & Hot Therapy Gel Pack
- Polar Active Ice Therapy Machine
- CryoCup Ice Massager for Targeted Relief
- NatraCure Gel Cold Wrap for Knees & Joints
- Vive Cold Therapy Wrap with Adjustable Straps